Content
This means that accounts with debit balances like assets will always increase when another debit is added to the account. Likewise, accounts with a credit balance, like liabilities, will always increase when another credit is added to the account. The T account is a fundamental training tool in double entry accounting, showing how one side of an accounting transaction is reflected in another account. This approach is not used in single entry accounting, where only one account is impacted by each transaction. T accounts are also used by even experienced accountants to clarify the more complex transactions. In double-entry bookkeeping, a widespread accounting method, all financial transactions are considered to affect at least two of a company’s accounts.

T-accounts can be a useful resource for bookkeeping and accounting novices, helping them understand debits, credits, and double-entry accounting principles. Unfortunately, any accounting entries that are completed manually run a much greater risk of inaccuracy. The process of transferring entries from General journal to General Ledger is known as ‘posting’.
A Small Business Guide to T-Accounts
My bank account is credited £4000, whilst the accounts payable account is debited £2000 and rent is debited £2000. Therefore, both debits and credits are equal in this transaction. Many companies have nowadays automated this process through the use of an accounting software. Once journal entries are made, they are automatically posted into respective ledger accounts.
- The left side of any t-account is a debit while the right side is a credit.
- Go a level deeper with us and investigate the potential impacts of climate change on investments like your retirement account.
- Thousands of people have transformed the way they plan their business through our ground-breaking financial forecasting software.
- Since most accounts will be affected by multiple journal entries and transactions, there are usually several numbers in both the debit and credit columns.
- In accounting, however, debits and credits refer to completely different things.
- T-accounts help to visualise the process making it clear what is occurring with each transaction.
They are a useful tool for both newcomers to accounting and veteran accountants alike to quickly map out the correct way to record a transaction. If you remember from part 1 and part 2, we went through how every debit must have a matching credit and vice versa. With Deskera you can effortlessly manage and oversee your invoices, credit notes, business expenses, financial reports all in one place. We at Deskera have spent over 10 years working with small business owners from across 100+ countries, to build accounting software that suits any type of business. One of the best accounting software for small businesses today is Deskera.
When Cash Is Debited and Credited
In double-entry bookkeeping, every transaction affects two accounts at the same time (hence the word double). One of these accounts is always debited, while the other always credited. Because T accounts are posted into the General Ledger of a business, they’re also commonly recognized as ledger accounts. Now these ledgers can be used to create an unadjusted trial balance in the next step of the accounting cycle. T-accounts can also be used to track changes to the income statement, which allows for creating accounts for a company’s revenues (profits) and expenses (losses). However, for liabilities and equity accounts, debits always represent a drop in the account, whereas credits always represent an increase.
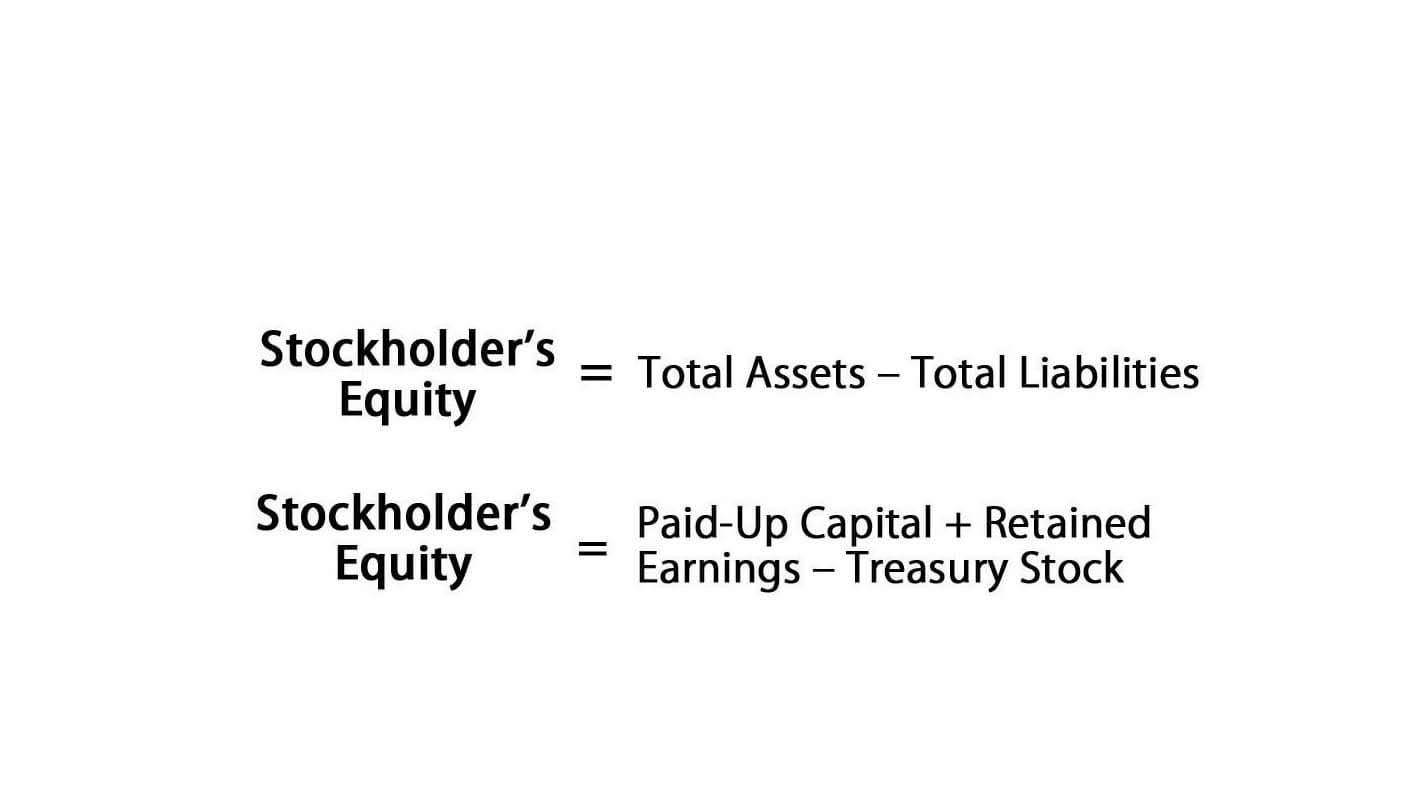
- A T-account is a tool used in accounting to visually represent changes in individual account balances.
- Each month, you prepare a trial balance showing your company’s position.
- If the final balance in the ledger account (T-account) is a credit balance, you will record the total in the right column.
- Manually maintaining a T account system is time-intensive and expensive.
- A T-account is an informal term for a set of financial records that uses double-entry bookkeeping.
- To illustrate all accounts affected by an accounting transaction, a group of T-account is usually clustered together.
Wages to employees are a business expense and decrease owner’s equity, so the Wages Expense account will be debited for $3,200. The asset Cash also decreases and gets a credit entry of $3,200. With that being said, the five most common types of accounts in financial accounting are assets, liabilities, expenses, revenue, https://www.bookstime.com/ and owner’s equity. First, these debit and credit entries are posted into the journal, as a journal entry. A T account (or general ledger account) is a graphical representation of a general ledger account. The general ledger is an accounting report that sorts and records a business’ financial transactions, by account.
Recording Error
In real business, We usually use T-accounts for adjusting entries like accruals, deferrals etc. This is very important to note that such accounts are only used in ‘accrual base of accounting system’ whereas there is no use of such accounts in cash base of accounting system. Gift cards have become an important topic for managers of any company. Understanding who buys gift cards, why, and when can be important in business planning.
After preparing your trial balance this month, you discover that it does not balance. The debit column shows $2,000 more dollars than the credit column. Once all journal entries have been posted to T-accounts, we can check to make sure the accounting equation remains balanced. A summary showing the T-accounts for Printing Plus is presented in Figure 3.10.
Everything to Run Your Business
The standard T-account structure starts with the heading including the account name. The left column is always the debit column while the right column is always the credit column. These errors may never be caught because a double entry system cannot know when a transaction is missing. For instance, a corporation that issues $200,000 worth of shares will see an increase in its asset account and a comparable increase in its equity account in its T-account.
- The main thing you need to know about debit and credit entries is that they are the equal and opposite sides of a financial transaction.
- A T Account is the visual structure used in double entry bookkeeping to keep debits and credits separated.
- This is posted to the Cash T-account on the credit side beneath the January 18 transaction.
- Another error is the incorrect recording of the transaction on the wrong side of the T or mistyping the numbers.
- If that’s not the case, make sure to double-check your books as you’ve probably made an accounting error along the way.
- My income account (revenue account) is being credited £2.50, increasing its value, making the transaction balanced.
T-accounts can be extremely useful for those struggling to understand accounting principles. T-accounts can be particularly useful for figuring out complicated or closing entries, allowing you to visualize the impact the entries will have on your accounts. One of the most well-known financial schemes is that involving the companies Enron Corporation and Arthur Andersen. Enron defrauded thousands by intentionally inflating revenues that did not exist.
T- Account Recording
Every journal entry is posted to its respective T Account, on the correct side, by the correct amount. Note that for this step, we are considering t accounts our trial balance to be unadjusted. The unadjusted trial balance in this section includes accounts before they have been adjusted.
It includes a list of all T-accounts and their balances, providing a comprehensive view of a company’s financial position. Ledgers can be maintained manually or electronically, and they serve as the basis for financial statements and other reports. A T account is the visual representation of accounts in the form of the alphabet T.
The liability Accounts Payable also increases by $2,500 and gets credited for the amount, since increases in liability result in a credit entry. The use and purpose of a T account is to help business owners visualize the amounts on each individual account. Splitting out debits and credits makes it easier to quickly spot things when looking at the ledger. The main thing you need to know about debit and credit entries is that they are the equal and opposite sides of a financial transaction. They’re simply words representing where cash is coming from, and where it’s flowing to, within a business.
